So far, humans have been developing technology as an assistive tool to perform jobs better under their control and supervision. That role of humans is about to change due to artificial intelligence (AI). Due to the potential to take over humans’ sensory and cognitive functions in work, artificial intelligence is perceived as the most disruptive force in history. However, despite the possibility, AI hype cycle poses an investment risk. Lack of clarity, early demonstration, Premature Saturation, the temptation of disruption, greed to make a quick buck, and the tendency to deceive are the underlying causes of fueling the AI hype cycle.
AI hype cycle refers to the sudden rise of inflated expectations due to early progress of unleashing disruption followed by rapid fall caused by technology development high barrier, leading to a slow growth phase after reaching the trough of disillusionment. Due to the AI hype cycle, AI Startups have suddenly risen, followed by speculation that about 85 percent of them would die within three years of their formation. The AI hype cycle is also the root cause of investors’ confidence’s sudden rise and fall, leading to buying highs and selling lows. Hence, it has become a source of market manipulation by big players to wipe out the hard-earned money of smaller ones.
Key takeaways
- AI hype cycle is about the sudden rise and fall of expectations about the potential of AI applications, followed by slow incremental advancement.
- AI hype cycle poses a risk of making disproportionate investments at the peak of expectations.
- Sudden fall also poses a risk of prematurely giving up AI innovations.
- AI hype cycle should be carefully monitored fro rational investment decisions.
Benefits of being aware and monitoring AI hype cycles:
- Avoiding irrational exuberance and frustration–for sure, early demonstration of human-like intelligence cause the hope of disruptive innovations. Hence, the temptation to make a disproportionate investment prematurely is a real possibility. Similarly, it also causes unrealistic frustrations about the sudden loss of current business and jobs.
- Avoiding investment at the peak and selling at the trough–monitoring of AI hype cycle is helpful for making investments at the peak of expectation and selling off at the trough.
- Pursuing a pragmatic path of exploiting possibilities–despite peak and trough, AI Innovation potentials are real. Hence, monitoring of AI hype cycle would help investors and policymakers to pursue deliverable possibilities.
Defining AI hype cycle
The hype cycle refers to the rapid rise and fall of expectations about technology possibilities in unleashing waves of Creative Destruction. Technology demonstration triggers the rise of confidence, reaching the peak of exaggerated expectations. However, the expectation does not stay at the height for long. Instead, it rapidly falls to the trough of disillusionment and starts rising slowly through the enlightening path.
Five phases of AI hype cycle, derived from the Gartner Hype Cycle, are as follows:
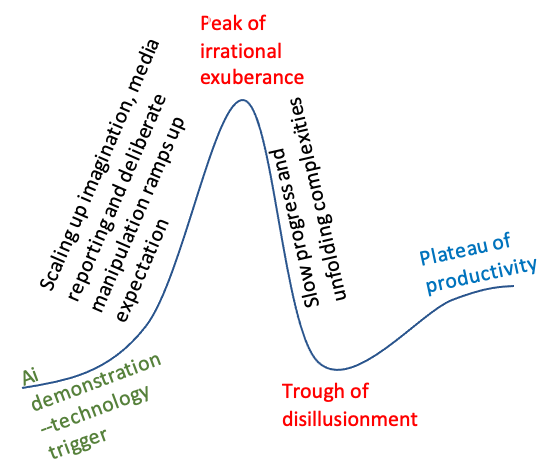
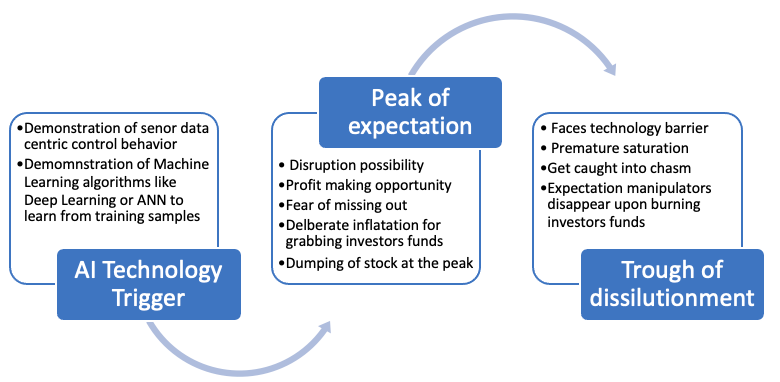
- Technology trigger–a demonstration of a proof-of-concept of human-like intelligence through sensors and machine learning by research labs, startups, and universities spurs imagination, media interest, and investment eagerness.
- Peak of inflated expectations–scaling up of potential in imagination space, analytical reports, deliberate attempts to fuel expectation to mobilize investment, and media reportings keep fueling enthusiasm, reaching the peak of expectation. At the peak, big players dump their AI stock holdings.
- Trough of disillusionment–slow or pause of growth of performance due to unfolding complexity of reality and non-linearity of technology advancement and disappearance of deliberate manipulation lead to creating questions about the technology feasibility and economic viability of potential applications. Consequentially, expectations turn into disillusionment, triggering a rapid fall–reaching the trough. Perhaps many potential killer AI applications like autonomous vehicles are now at this stage of the hype cycle.
- Slope of enlightenment–the science of demonstrations starts getting clear, and people develop more realistic understanding about what could be a deliverable target and at what space progress could be made. Instead of a sudden rise, potential applications start incrementally growing.
- Plateau of productivity–through sustained incremental growth, target AI innovations start reaching maturity, resulting in diffusing deeper and reaching the peak of performance.
Underlying causes of the AI hype cycle
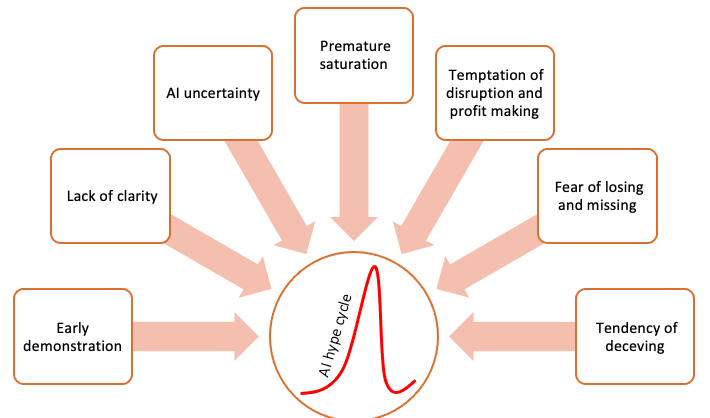
There have seven primary reasons underpinning the AI hype cycle:
- Lack of clarity—insufficient knowledge about human intelligence and the complexity of tasks leads to developing an unrealistic understanding of the difficulty of imitating human intelligence.
- Early demonstration—easy demonstration of human-like intelligence through simple sensors, data analysis, and control algorithms builds confidence in replacing humans’ role in the control loop of machines. Similarly, the success of machine learning (ML) algorithms or neural networks through training samples gives the impression of developing human-like machine learning capability.
- AI uncertainty—despite early demonstration, AI suffers from significant uncertainty in technology capability, detailed breakdown of tasks, nature of human intelligence, and complexity of imitating human-like intelligence. This factor has been a considerable cause of the quick fall in expectations.
- Premature saturation—due to lack of clarity and AI uncertainty, early progress does not grow linearly. Instead, in most cases, the growth tends to saturate before crossing the threshold level.
- Temptation of disruption and profit making—upon making and observing the early demonstration, the temptation of causing disruption and making profit surfaces, resulting in inflated expectations.
- Fear of losing and missing—the demonstration of the replacement of the human role in work causes fear of losing jobs and businesses. On the other hand, fear of missing the next wave also creates stimulation of jumping onto the new wave.
- The tendency of deceiving—some intelligent people, who appear shrewd, take advantage of the previous six factors to inflate expectations for alluring investors with the proposition that AI waves of creative destruction are about to unfold. However, they are cunning enough to dump their shareholdings at the peak of inflated expectations.
Examples of the AI hype cycle
- Humanoid robots take over service jobs–In the 1920s, Eric humanoid robots created high sensations about the possibility of developing human-like creatures to do all kinds of dull jobs. However, the sensation disappeared within a few years, along with Eric. Since then, we have witnessed one after another wave of the humanoid robot hype cycle. Recent ones are Sophia, ASIMO, and many more.
- Autonomous vehicles disrupting jobs and car ownership model—in the middle of the 2010s, the demonstration of autonomous vehicles by Google and others created the sensation of disrupting automobile driving jobs and car ownership model. Hence, the hype cycle inflated, leading to reaching inflated expectations and pouring billions of dollars into investment. However, upon getting caught in the chasm, it did not take long to plunge into the trough of disillusionment.
- AI for medical prescriptions—Upon demonstrating Watson’s apparent AI capability, IBM embarked on developing an AI cancer prescription solution. However, after spending $2 billion, the expectation got lost into disillusionment.
- AI disruption in education—during COVID the popularity of online lectures and the demonstration of machine learning for offering adaptive content, the hype of AI disruption in education started to get momentum. However, the fall of India’s Edutech Byju’s valuation from $22 billion to $5 billion over two years indicates a rapid fall in expectations.
- ChatGPT for disrupting the knowledge profession—ChatGPT and other machine learning demonstrations of large language models have started to fuel a hype cycle of unleashing disruption to the jobs of the knowledge profession.
Investment euphoria
Technology possibility is the underlying cause of triggering the rise of a creative wave of destruction—causing Wealth annihilation and accumulation. Due to this, tiny startups grow, and behemoths disappear. Hence, often, investments in startups grow at a very high rate. On the other hand, the shareholder value of established firms disappears due to the rise of the next wave of creative destruction. Hence, there is a natural tendency to believe in and ride on new waves.
However, not all innovation waves keep growing linearly. Often, they suffer from technology uncertainty. Sometimes, they also get caught in the chasm. Besides, there is concern about manipulating expectations to increase the price of shares and dump them at the inflated price. Hence, due to the high level of uncertainty and strong belief in AI’s disruptive power, there is an increased risk of suffering from investment euphoria caused by the AI hype cycle.
Negative Consequences
- Distraction of attention from realistic possibilities
- Irrational target setting and response, including disproportionate valuation and funding
- Manipulation of expectation for abusing funds and dumping stocks at a very high price
- Loss of investment, notably by small investors
- Unexpected AI Winter
- Risk lack of R&D funds before the full potential is exploited
How do we avoid it?
We need to pay attention to AI possibility and uncertainty to avoid missing the next wave and riding the hype cycle. We need to educate ourselves about what it would take for AI technology to unleash Creative waves of destruction. The knowledge of technology innovation dynamics caused by the evolution of technology and consumer preferences and competition should get a priority. Due to likely disruptive consequences, we must not miss the AI wave. Similarly, we should not ride the AI hype cycle as it will likely cause a significant loss of investment.




