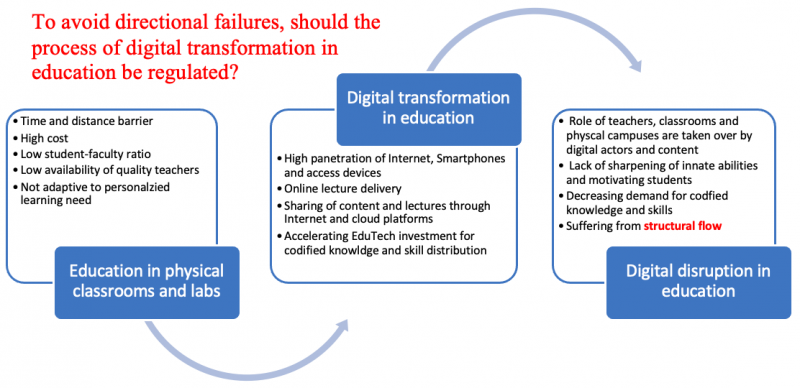
Attempts to adopt digital technologies like personal computers, the internet, digital content, and multimedia projectors in education started in the early 1990s. Their roles were limited to offering assistive services to conventional classroom-based approaches. However, the rapid adoption of online lecture delivery during the Covid time demonstrated the possibility of replacing classrooms, lectures, and textbooks with online education. This trend has continued to replace physical classrooms with online lectures, teachers with digital characters like avatars or robots, pens and pencils with keyboards, and books with digital content. Consequentially, digital transformation in education has been unfolding by adopting digital technologies for reinventing teachers, books, lecture delivery, assessment methods, and operations of academic institutions.
Of course, there have been many benefits of digital transformation in education. Notable ones are (i) no need to travel and be physically present in a classroom, (ii) lectures, contents, and other resources are always available online, and (iii) real-time performance analysis and personalized services by AI. Hence, digital transformation breaks down distance, time, quality lectures, and teacher-student ratio barriers.
Despite all these benefits, is digital transformation in education free from limitations? Should we be concerned with the disadvantages of online education? How does education in digital space sharpen innate abilities like vision and multi-limb coordination, accentuate punctuality, and motivate learners? Should we be concerned with smartphone addiction, frequent interruption, and attention span?
Despite the risk of being a double-edged sword, investment in digital transformation in education is increasing. The EduTech market will likely hit over USD 400 billion by 2025. Consequentially, digital transformation in education risks being a vendor-led technology push agenda, compromising the long-run outcome. Hence, it’s time to focus on leveraging technology to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of education instead of weakening the core.
Key takeaways
- Digital transformation in education by leveraging the internet, smartphones, tablets, and PCs, digital content, video conferencing, and other software applications has already started.
- Online education has been gaining acceptance due to multiple benefits like overcoming distance and time barriers.
- Due to benefits and growing EduTech investment, digital transformation in education may lead to digital disruption in education.
- Despite many benefits, online classrooms and other digital means of imparting education have limited scope for sharpening innate abilities, inspiring students and maintaining attention span.
- Codified Knowledge and skills delivered by online education are losing market value due to the ease of software-centric automation.
- Digital disruption in education through the replacement of pen with keyboards, classrooms with online lecture delivery, and teachers with digital characters like avatars run the risk of suffering from structural flaws.
Contents
- Envisioning digital disruption in education
- Relevance of education and technology shaping the future of work
- Defining digital transformation in education
- Lecture halls to online learning—is the evolution free from limitations?
- Unfolding digital transformation in education
- Upcoming digital technologies in education
- Benefits of digital transformation in education
- Digital disruption in education suffers from structural flaws
Envisioning digital disruption in education
Let’s ponder a bit to comprehend the long-run goal of digital transformation in education. Due to the technology possibility and profit-making urgency of the EduTech community, where is it heading? Let’s examine the following scenario, which we may call digital disruption in education:
Physical education facilities completely disappear: Students will no longer attend physical classes. Due to the many benefits, they will have personalized education through digital platforms. The physical presence of schools, colleges, and universities disappears entirely.
No relevance of pen, pencil, and paper: Students no longer need to write using pen or paper. Either they type or speak to machines, or computers read their minds. Hence, the relevance of pen, pencil, and paper in education will disappear entirely.
No need for humans to deliver lectures: Due to numerous benefits, digital characters or Avatars will be taking the role of human teachers to deliver lectures, offer feedback, and make real-time assessments of students’ performance. Hence, digital transformation in education leads to human-free educational services.
For sure, such an envisioned scenario appears to be digitally feasible. Of course, there have been benefits. Besides, massive EduTech investment has a profit-making urgency to keep pushing such a possibility. However, does digital disruption in education in preparing students for future of work suffer from structural flaw?
Relevance of education and technology shaping the future of work
Education has a long history of serving diverse purposes. However, in modern times, the primary purpose of education has been to drive economic growth by turning students into human capital. Hence, education needs to sharpen innate abilities, increase knowledge stock, enhance learning abilities, improve creativity, enhance empathy, and accentuate passion for the perfection of the students. Not all kinds of professions require these human capital attributes equally. Moreover, technology has been changing the role of humans in work. Therefore, to understand the advantages and disadvantages of digital transformation in education, we must focus on understanding the human role in work. More importantly, we should focus on the trend of technology transforming the human role in work. Besides, technology does not face equal difficulty transferring different human roles to machines.
In the 1950s, engineers used to spend a substantial amount of time in the office to solve mathematical equations for optimizing designs. That role has mostly been taken over by software. Similarly, software has taken over the role of data processing in different functional areas of corporations—causing hollowing out the middle effect. Besides, due to Innovation evolution, ideas are having a growing role in economic value creation—demanding empathy and Passion for Perfection. For example, in the semiconductor industry, as high as 50 percent of economic value distills from design knowledge and ideas.
Despite the common belief that technology has been killing labor-intensive manufacturing jobs, technology has been empowering the low-skilled workforce for factory jobs. Due to job division, organization of manufacturing tasks as production lines, and automation of codified knowledge and skills, manufacturing demands only innate human abilities. Besides, due to the high complexity of automating innate abilities, robots are leaving mundane jobs for humans. Hence, sharpening natural abilities lead to growing productivity and increasing barrier to automation. On the other hand, due to the ease of automation of codified knowledge and skills, machines are taking over white-collar jobs.
Defining digital transformation in education
All goods and services have been growing through digital transformation. Hence, the transformation of education through digital technology possibility is no exception. Of course, the space varies from incremental advancement to Creative Destruction. Digital transformation in education refers to the process of creating the flywheel effect from the leveraging of technology possibilities for transforming education. This transformation may lead to the Reinvention of teachers as digital actors, physical presence by connectivity, classrooms by online platforms, and books by digital resources. Consequentially, massive disruption will unfold, likely making the ways we deliver education and run the education system obsolete.
Digital transformation in education has the potential to enhance teaching and learning. Delivery of educational services using technology could improve effectiveness and efficiency. It will likely support student progression and enhance the quality of teaching methods like online learning.
Lecture halls to online learning—is the evolution free from limitations?
The evolution of education has been unfolding through the migration from lecture halls to online learning. We are already at the dawn of ushering in online learning. It’s becoming an increasingly popular option for students due to the flexibility to pursue their education on their terms. In some cases, academic institutions are finding it as a cost-cutting means.
As students can access course materials, lectures, and assignments from anywhere over the internet, access to lessons and course materials is no longer limited to physical locations or rigid class schedules. Besides, online discussion forums, video conferences, and virtual group projects take collaboration to a new height. Unlike in the past, students can engage with their peers and instructors anytime from anywhere–in ways that were impossible before. Hence, by referring to all these advantages, EduTech companies have been promoting online education as a viable alternative.
Unfolding digital transformation in education
Like all other transformations, digital transformation process in education has already started as incremental advancement. For example, books in digital format are widely available. COVID time widely used online lectures are being practiced now and then. Archive of content as digital library has already taken root. Experimentations of physical and virtual robots as teachers’ replacements have already started. Notably, their major transformations have already unfolded with the potential of reaching digital disruption in education.
Reaching out with online-only courses: Massive open online courses (MOOCs) have already dented the barriers of cost and distance to access quality lectures and content. The MOOC market is expected to keep growing at a CAGR of 34.54%, reaching over US$7 billion by 2027. However, low completion rate is a cause of concern.
Personalized education: Measuring student learning using data analytics has the potential of overcoming a one-size-fits-all model barrier, making adaptive learning a reality. Online learning offers real-time insights into student’s performance, opening the door to tailoring the educational content to fit individual student’s needs. Instead of the necessity of adapting to the standard teaching style and content, the digital platform has the freedom to adjust to the unique needs of each student. It’s encouraging to note that students in the adaptive learning program at HarvardX demonstrated 19% greater knowledge gain in assessment.
Digital transformation in lifelong learning and upskilling: Due to the rapid pace of change of skill demand, lifelong learning for upskilling has been accelerating. However, people at work face difficulty fitting into the fixed schedule of offering courses. Finding time to travel during or after office hours is also a barrier. Hence, online education has been gaining traction to meet the lifelong learning need for continuous upskilling. Already, micro-credentials and digital badges are increasingly becoming prevalent.
Upcoming digital technologies in education
Digital transformation in education has been reaching beyond the advantage of online learning. Increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) has been adding further momentum to unleash digital disruption in education. Providing personalized recommendations, adaptive assessments, and intelligent feedback through AI will likely revolutionize the learning experience.
Furthermore, learning in a virtual reality (VR) augmented reality environment is poised to add further momentum to the wave of digital transformation, turning it into digital disruption in education. Leveraging these immersive technologies may lead to the creating a realistic and interactive learning environments to explain abstract concepts as near real-life experiences. For example, students may travel through the complex blood circulation system or dive into the molecular structure of materails, plants and animals.
Benefits of digital transformation in education
As already mentioned, digital transformation in education is fueled numerous benefits. Notable ones have been (i) overcoming the barrier of time and distance, (ii) reducing cost, (iii) adaptive learning due to AI and ML, (iv) ease of lifelong learning, and (v) learning complex concepts in an immersive environment.
However, to leverage these benefits, students should be in charge of themselves. Hence, they should pay attention to (i) staying organized, (ii) participating actively, (iii) seeking help when needed, (iv) developing digital literacy, and (v) avoiding technology addiction, frequent interruption, excessive screen time, and social isolation.
Digital transformation in education suffers from structural flaws
Codified knowledge and skills are losing market value: Due to inherent limitations, learning in the digital space mainly focuses on efficiency in delivering codified knowledge and skills. Due to the ease of automation with software, the market value of codified knowledge and skill has been rapidly diminishing.
Online education faces the barrier to sharpening innate abilities: Humans are blessed with 52 natural abilities. They belong to four categories: i) Cognitive, (ii) Physical, (iii) Psychomotor, and (iv) Sensory. According to O*net analysis of 923 occupations, they play essential roles. Unfortunately, education in digital space has limited or no ability to sharpen them. Instead, digital disruption in education runs the risk of blunting them. For example, the replacement of a pen or pencil with a keyboard will lead to rigidity of fingers, making online learners less eligible for jobs requiring dexterity such as surgery.
Nurturing empathy and passion for perfection in digital space faces limitations: From elderly care to driving the evolution of innovation, future jobs will increasingly demand empathy and passion for perfection. Unfortunately, education in the digital space does not have the scope to build these two vital abilities.
Robots or Avatars are not eligible for motivating and sharpening imagination: Due to the rapid automation of codified knowledge and skills, graduates will require internal spirit to keep upskilling and moving from one job to another. Besides, increasing demand for R&D jobs will require motivation and imagination. So far, studies indicate that machines are not eligible to connect to the human mind and soul.
Technology addiction, frequent interruption, and lack of punctuality undermine digital possibilities: Despite many benefits, the ease of online learning opens the freedom of procrastinating and getting frequent distractions, resulting in a shortened attention span and low productivity in learning.
Should digital transformation in education lead to digital disruption?
Digital transformation in education has already established its visible implications. Beyond the COVID era, online learning has not disappeared. Besides, using learning management systems (LMSs) like Canvas has become integral to physical classrooms. Sharing study materials and recorded lectures through such LMSs has become common. On the other hand, MOOCs and other online platforms have been gaining momentum.

As explained, digital transformation in education has been progressing due to many advantages. Besides, EduTech investment has accelerated, and a growing number of academic institutions and degree programs solely exist in the digital space. Such a trend indicates the temptation of turning digital transformation in education into digital disruption of education. Besides, digital disruption in other industries, such as music and video content distribution, could inspire to do the same in education.
As explained, digital disruption in education runs the risk of suffering from structural flaws. Hence, the prudent approach to benefiting from digital transformation in education should focus on augmenting teachers, classrooms, and laboratories instead of completely replacing them. Besides, the profit-making urgency of EduTech community poses real risk of meritless reliance on digital means in education. Therefore, the temptation of digital disruption in education should be regulated. Otherwise, we run the risk of digital transformation in education detrimental to preparing graduates for the future of work.




