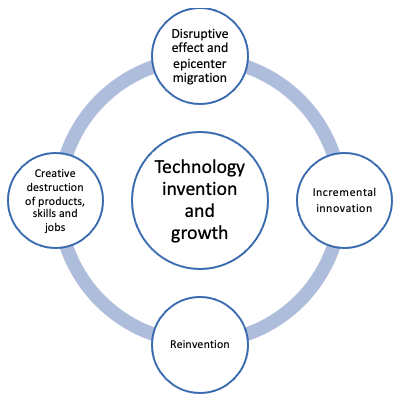
The first industrial revolution unfolded due to technology transformation. Since then, it has been intensifying in recreating products and how we get our jobs done. Due to this, little Startups have been attaining market power and dislodging incumbent behemoths. Innovation epicenters have been migrating, causing a rise and slowing down economies. Technology transformation refers to leveraging technology possibilities to benefit from Getting jobs done better by transforming products, production processes, delivering channels, business models, employment, and market positions.
Examples of technology transformation
Notable examples of technology transformation are mobile phones, smartphones, word processors, digital cameras, smart television, automation & robotics, e-mail, and the World Wide Web. Emerging technology transformations include electric vehicles, autonomous vehicles, digital currency, working and socialization in the metaverse, hydrogen fuel, renewable energy, and many more.
Due to technology transformation, existing jobs and skills have become obsolete. For example, due to e-mail, there has been no demand for telegram services. Hence, related jobs have disappeared. Similarly, jobs for making and printing films for photography are no longer available. Technology transformation also creates jobs–new types of jobs. Notably, high-paying R&D and innovation jobs are created to advance technology transformation.
Technology transformation offers the opportunity for startups to reinvent mature products. Ironically, frequently, incumbent profit-making firms from matured products avoid Reinvention possibilities. Consequentially, they suffer from Disruptive innovation effects while startups rise by embracing technology transformation. For example, while Sony rose, Kodak, RCA, and others suffered.
How does technology transformation take place?
Technology transformation unfolds in the form of Incremental innovation and reinvention. Although reinvention is at the core, incremental innovation plays a vital role. The cumulative effect of the gradual advancement of technology possibilities often leads to a transformative impact. For example, Toyota’s approach of leveraging batteries in a step-wise manner has been leading to making the internal combustion engine obsolete.
Creative Destruction, disruptive innovation, and radical innovation are natural outcomes of technology transformation. For example, the transformation of mobile handsets has led to the rise of smartphones as an example of creative destruction and disruptive innovation. Similarly, the word process has been a radical innovation due to the unleashing of its creative destruction force on typewriters and manual page setups. And it has become a disruptive innovation as new entrants like Microsoft and Apple succeeded in unleashing its radical transformative power.
Digital transformation
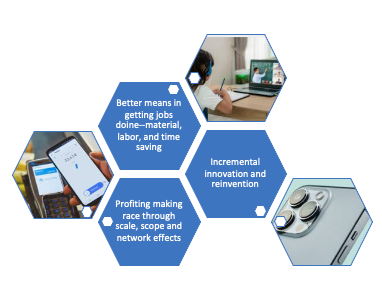
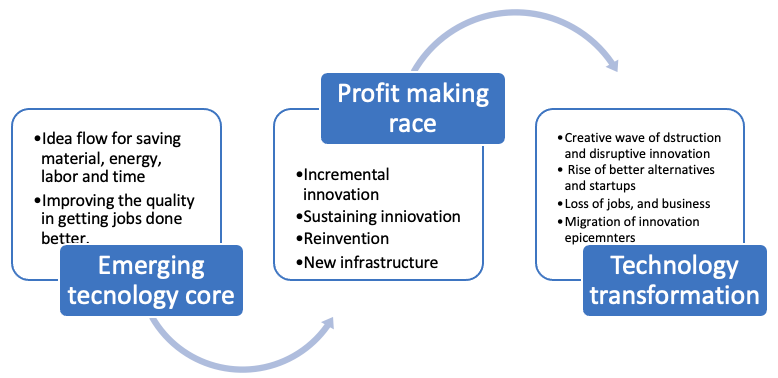
Digital transformation is the adoption of digital technology in products and processes to fundamentally changing the way we create, deliver, and capture value. Instead of a suddenly occurring phenomenon, it unfolds as a process, from incremental change to disruptive consequence. Digital transformation is a process of advancing products, production processes, and delivery channels from incremental innovation to reinvention by adopting digital technologies to help customers in getting jobs done better. It offers entry opportunities, advancing competitiveness, creating a flywheel effect, and unleashing disruptive innovation. Due to the zero cost of copying software and digital assets, and labor, material, energy, and time-saving roles, it’s a tool for making business scalable. Hence, from a humble beginning, digital transformation unfolds as radical innovations.
Furthermore, due to high Economies of Scale, scope, and network effects, winners in digital transformation may take all. Due to the amenability of making products better and cheaper, the winner may succeed in attaining market power for monopolizing the market. For example, Microsoft has a monopoly in office computing due to digital transformation. Similarly, due to leveraging digital transformation, Amazon has attained market power in e-books, cloud computing, e-commerce, and a few other businesses.
AI transformation
Artificial Intelligence technology is the fusion of a series of component technologies like sensors, data science, software, learning algorithms like deep neural networks, low latency communication, and so on. To offer better alternatives, AI transformation targets to take over the human cognitive role in the operation and production of goods and services. For example, by replacing humans in driving, AI technology would like to transform how we use automobiles. Similarly, by replacing the cognitive role of human doctors, AI would like to offer more accurate disease diagnoses and prescriptions. Consequentially, AI will transform jobs and the ways we serve diverse purposes.
Customer experience transformation in getting jobs done
At the core of the success of technology transformation has been the resonance between technology possibilities and urgency in meeting unfolding customer preferences. For example, Apple’s Macintosh computer became a typical example of technological transformation because there was a response between customer preferences in using GUI and the rise of microchip power to support it. Similarly, the iPhone’s success is rooted in this reality.
Technology transformation causes rise and slowdown of firms and nations
The effect of technology transformation is not only limited to the transformation of products and processes in offering better means to customers in getting jobs done. It has strong implications on the rise of startups and the slowdown of incumbent behemoths. It happens due to the behemoth’s profit-making success from matured products and processes and the inherent high risk of unproven technology possibilities. Thus, there is a natural tendency for migration of innovation epicenters across the boundaries of firms and nations, resulting in a rise and slowdown. For example, due to the transformative effect of semiconductors, the innovation epicenter of consumer electronics migrated from the USA and Europe to Japan and South Korea. Similarly, the rise of electric vehicles will likely migrate the automobile innovation epicenter from Europe and the USA to China and Japan. Due to this reality, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan have risen to high-income status.
Winning the technology transformation race
Here are seven steps for winning the technology transformation race:
- Target technology core at the early stage: technology core should be amenable to progression, and entry must be made at the early stage.
- Paying attention to customer preferences: the focus should be on understanding customer preferences and leveraging technology possibilities to address them better.
- Picking suitable timing and creating a Flow of Ideas: suitable time is vital for leveraging externalities. A flow of ideas must be created to create the snowball or flywheel effect for unleashing radical innovations.
- Ensuring synchronized response: multiple stakeholders, including component technology suppliers, infrastructure developers, products and process innovators, and policymakers, must synchronize response.
- Creating scale, scope, and positive externalities: To win the competition, the focus must be on creating scale, scope, and positive externalities from technology transformation.
- Detecting and crossing the chasm and avoiding the hype cycle: in pursuing technology transformation, the risk of getting caught in the chasm is relatively high. It happens due to getting stuck to progress further. Such a reality creates a hype cycle, which must be avoided or overcome.
- Attaining market power for price-setting capability: for winning the technology transformation race, market power must be attained so that profit-making price-setting capability surfaces.
Technology transformation drives innovations and creates Wealth by offering better alternatives. Consequentially, skills, jobs, firms, industries, and the economy keep experiencing creation and destruction. Hence, uncertainty is an inherent attribute of technology transformation.