There has been a growing urgency for science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) education and research. Although Muslims’ STEM excellence in the Middle Ages was due to the urge to know the creation, the modern day’s importance of STEM stems from creating economic prosperity from STEM. Hence, getting high-paying jobs in big technology firms and leveraging technology possibilities through turning embryonic Startups into mega success have been the significant drivers among students in pursuing STEM education and careers. On the other hand, due to the positive correlation between STEM indicators and high-income status, less developed countries have been showing increasing importance of STEM. Besides, new economic growth theories, like Paul Romer’s endogenous growth theory, are paying attention to linking long-run economic growth to technological ideas. Hence, the importance of STEM has been finding a central position in the mission of individuals, firms, and nations in driving economic prosperity.
Despite STEM’s decisive role in creating high-performing firms and good-paying jobs and driving less developed countries to high-income status, reality raises questions about the natural correlation of STEM indicators and economic growth. For example, irrespective of the greatness, all inventions begin the journey in embryonic form. Initially, they offer little or no merit for practical purposes, let alone creating prosperity. On the other hand, firms attaining high-level success through scientific discoveries, inventions, technological advancement, and superb engineering performance fail to sustain success. However, to our surprise, although more than ninety percent of startups fail to reach profit after getting needed funding, a few succeed. Even their successes cause destruction to high-performing firms having financial solid, engineering, Innovation, and manufacturing track record. Besides, although advanced countries suffer from a scarcity of STEM graduates, less developed countries have been struggling with growing unemployment among engineering graduates.
Outline
- Turning STEM possibility into prosperity—economics and management challenges
- Jobs to be done—STEM meets relentless urgency
- Rising Importance of STEM—Historical Perspective
- STEM competence not good enough—questioning STEM progress in creating Wealth
- Economics and Management of STEM
- Importance of STEM Policy
Turning STEM possibility into prosperity—economics and management challenges
As explained, the importance of STEM in modern times is due to its track record of driving economic prosperity. It’s worth noting that Muslims could not sustain their scientific excellence due to their failure to create wealth from STEM. Besides, despite attaining the edge in science and technology, Russia could not leverage it to drive economic prosperity due to a command-driven economy. On the other hand, Europe-led Western countries have shown remarkable performance in creating wealth from STEM. It happened due to market economic policies intensifying profit-making competition from a flow of STEM-powered ideas.
Competition plays a vital role in growing technological possibilities through a Flow of Ideas to unleash economic value. But it also creates risk in profiting from investment. Competition adds to the uncertainty about the growth of technologies into profitable business. As a result, management challenge increases in creating economic value from technology possibilities. The challenge expands from managing R&D to winning the competition race in the globally connected competitive market.
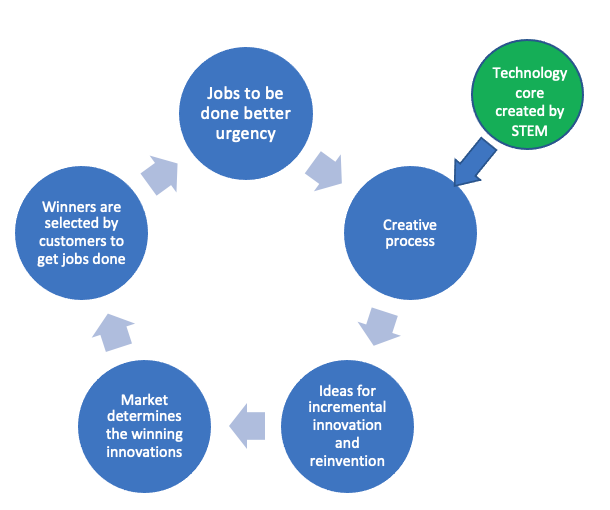
Furthermore, due to the endless possibilities of the rise of Reinvention waves as Creative waves of destruction and superior performance in incremental advancement, success does not naturally sustain. Besides, winning a race by offering better quality at less cost due to the flow of ideas has a natural tendency to end up in the winner-take-all-all market. As a result, many high-performing firms suffer from loss because the winner takes all.
In addition to technology uncertainty and unpredictable competition responses, how to respond to unfolding consumer preferences is a management issue. Besides, public policies are vital in opening and closing the door to creating economic value from STEM. Let’s look into pertinent economics and management issues for driving prosperity from STEM knowledge and ideas.
Jobs to be done—STEM meets relentless urgency
The importance of STEM in creating economic value should begin the journey by focusing on how customers use STEM competence. Customers derive economic benefits from the usage of products in getting jobs done. And they have been increasingly looking for better products to perform those jobs. It happens that technology empowers us to innovate products, improve their quality, and reduce the cost. Hence, technology is essential. Besides, technologies’ capability of enhancing the quality and lowering the cost tremendously helps producers meet conflicting requirements—making a profit by offering better quality at less cost. Therefore, the importance of technology in creating economic value for producers and consumers is paramount.
For producing ideas, STEM competence is not good enough. Yes, we need creativity to create ideas out of STEM competence. However, in the absence of urgency, it does not work. The urgency of increasing profits by offering increasingly higher quality products at decreasing cost is an essential requirement for idea production.
Although the cost of producing ideas is high, the cost of adding them to each product unit is often meager. Notably, in software-centric innovation, the marginal cost is almost zero. The profit-making opportunity grows with the scale if the marginal willingness to pay due to adding an idea is more than the cost. Hence, management faces the challenges and opportunities of profiting from idea production and commercialization. Because of profit-making opportunities, there is a growing race for R&D financing, creating high-paying jobs for STEM graduates.
As there is a possibility of opening and sustaining a highly scalable path in driving revenue and profit, management professionals are also finding high-paying jobs by leveraging technology. Furthermore, due to the reality of science, the endless frontier, this journey of profiting from a flow of technology ideas, creating consumer surpluses and high-paying jobs will continue.
For Further Clarity
- Jobs to be done—driving quality of living and wealth
- Importance of Technology—fueling innovations in jobs to be done
- Importance of Creativity—how to fuel for driving innovation and growth?
- High-Income jobs—Leverage Technology Possibilities
- Science the Endless Frontier—for driving prosperity
Rising Importance of STEM—Historical Perspective
Due to the advancement and leveraging of STEM, innovators found a scalable path to making products better and cheaper. As a result, industrial production accelerated, giving birth to the first industrial revolution and industrial economy. Due to continued quality advancement and cost reduction due to STEM, the industrial economy has been growing in scale and scope. In driving this progress, the evolution of technology has been essential.
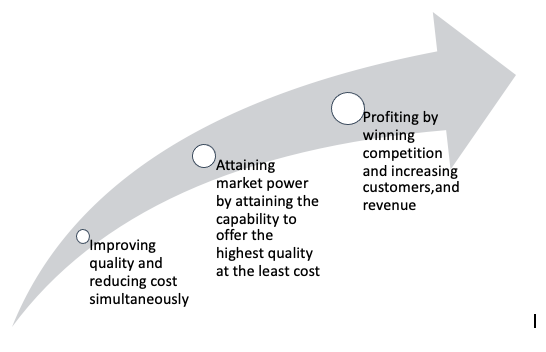
In the preindustrial age, inventions were not scalable. Our ancestors had primitive means of getting jobs done. Hence, their living standard was far poorer than we enjoy today. Therefore, they had an urgency to scale up inventions and innovations. Despite the progress of science in the Middle Ages by the Muslims, science remained decoupled from advancing technology and engineering in offering better means of getting jobs done. However, the Europeans succeeded in leveraging science to turn Craftsmanship into Engineering and tinkering into systematic investigation. That resulted in scaling up innovations. Besides, adopting Market Economy principles intensified the advancement and leveraging of STEM in offering increasingly better products due to profit-making incentives. Such development is marked in the history of STEM as the rise of craftsmanship of the Industrial Age into the Industrial Revolution.
The evolution of technology has been playing a critical role
At the root of the growth of the industrial economy and our quality of living standards has been the success of the evolution of technologies. For example, the Steam Engine kept evolving, powering the first industrial revolution from 1760 to 1880. But it was born in an embryonic form far before the advent of the Industrial Revolution. Like the steam engine, the light bulb, the television, the computer, and many other inventions got birth in primitive forms. At the early life cycle stage, they had little or no capability to contribute to strengthening the industrial economy. But all these technological inventions have evolved due to the advancement and leveraging of STEM. Consequently, innovations have been improving in quality, cost, and number—offering increasingly better means of getting jobs done.
Profit-Making Incentives Intensifies the Importance of STEM
Scientific discoveries powering technological inventions, upgrading craftsmanship into Engineering, and developing mathematics have not been sufficient in driving prosperity. The profit-making incentive of improving primitive inventions and innovating products and processes has been playing a vital role. Hence, the role of the market economy has been critical in advancing and leveraging STEM. Due to profit-making incentives offered by the market economy, competition in creating a flow of ideas for evolving inventions and innovations has been a critical driver for advancing the industrial economy. Consequentially, the race to win in innovation has intensified. However, such a race has a natural tendency for Monopolistic market power accumulation. Consequentially, the race to profit from STEM leads to evaporating competition, raising serious economic Governess issues.
For Further Clarity
- History of STEM— powering the rise of nations by creating idea economy
- Industrial Economy—role of STEM
- Technology Evolution—why, how, and examples
- Profiting from Innovation—the role of the market
- Winning Innovation—how to excel and sustain
STEM competence not good enough—questioning STEM progress in creating wealth
The rise of Western economies shows a positive correlation between STEM indicators and economic prosperity. If that correlation were naturally true, why couldn’t Russia drive prosperity out of STEM? Besides, why could not Muslims leverage STEM success into economic prosperity, ushering in the Industrial Revolution far earlier? Furthermore, why have the growing number of STEM graduates in India, Bangladesh, and many other less-developed countries been suffering from a lack of job opportunities? Hence, STEM competence need is not good enough to establish the importance of STEM.
Regardless of the quality, Jobs for STEM graduates do not naturally appear in all economies. Unless firms and nations keep driving economic growth from discoveries, inventions, and innovations, Jobs for STEM graduates will not sustain growth. Yes, leveraging technology from usage creates some jobs for making, operating and repairing. But those are not high-paying jobs for STEM graduates.
Quality jobs for STEM graduates are created once economies get into the race to outperform incumbent top performers through superior incremental performance. Besides, nurturing a creative wave of destruction out of the reinvention of matured products lead to new STEM jobs and higher-quality alternative at less cost. Hence, STEM education is not sufficient. Even creativity in producing ideas is not enough. STEM education should be leveraged to generate a flow of ideas to create a growing scale effect of existing products. Besides, to drive prosperity, grassroots innovation having latent potential must be scaled up through systematic exploitation of STEM. Hence, innovation ranking by measuring indicators like STEM graduates, publications, and patents is often misleading.
For Further Clarity
- Jobs for STEM Graduates—growing insecurity and reward.
- Leveraging Technology—from usages to advancement.
- Creative Wave of Destruction—fueled by STEM, but not good enough.
- STEM Education—not good enough for prosperity.
- Economies of Scale Effect— highly matters.
- Innovation Ranking—is it misleading?
- Scaling up Grassroots Innovation
Economics and Management of STEM
As explained, the growing importance of STEM has been due to the proven possibility of creating wealth by leveraging STEM. To make it happen, the focus should be on economics and engineering. Products and processes should be engineered to offer increasingly higher quality at decreasing cost. To profit from such an exercise, a competition race must be won by leveraging the economics of technology.
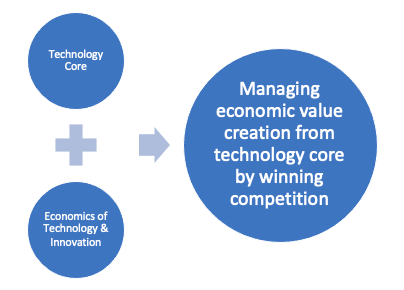
Winning the competition race is vital for turning the investment into wealth. Hence, knowledge and ideas are not sufficient enough. As more than 75 percent of products and over 90 percent of startups retire without producing profitable revenue, there is a high risk of turning STEM competence into economic prosperity. Hence, Economic Growth Theories like Paul Romer’s theory of ideas and objects for producing economic output run the risk of misguidance. Often, such theories give the temptation that there is a natural correlation between STEM education and R&D investment, and economic growth.
There is no denying that the STEM Economy may offer endless frontier, as articulated by Vannevar Bush. However, the endless flow of science is not sufficient. In the race to provide better quality products and get jobs done better, the focus should be on managing ideas for sustaining success. Hence, there is a need for technology management and a stronghold on innovation management. How to create technology ideas systematically so that the flow of ideas sustains is critical to drive prosperity from STEM. Such competence is also at the core of succeeding with technology startups, as scaling up startups demands a flow of ideas to nurture embryonic ones.
For Further Clarity
- Economics and Engineering—winning innovation race.
- Economics of Technology—profiting from technology possibilities.
- Economic Growth Theory—STEM offers endless paths.
- STEM Economy—endless frontier.
- Managing Ideas—for sustaining success.
- Management of Technology—turning uncertainties into profit.
- Technology ideas—how to create and sustain the flow?
- Innovation Management—systematic progression
- Technology Startups—managing to scale.
Importance of STEM Policy—for driving prosperity out of STEM
The rise of Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan has been due to the leveraging of STEM. History also raises questions about why it could not UK-led Europe sustain economic supremacy despite the success of ushering in the Industrial Revolution. Did the USA rise by causing the fall of the UK and the rest of Europe? Furthermore, did the rise of Taiwan’s semiconductor industry cause damage to the USA’s Silicon Valley’s success?
Due to the winning race, STEM has been playing a critical role in the rise and fall of nations and economies. Besides, although the industrial revolution powered by STEM is the root cause of growing pollution, emissions, and accidents, STEM is also the solution for sustainable development. Hence, technology policy for sustainable development is a burning issue.
All the world’s nations would like to sustain economic growth, reaching and staying in high-income states. Despite their positive role, natural resources and labor are not a means for all to get rich. On the other hand, STEM does not offer a natural correlation to wealth creation in a globally connected competitive market economy.
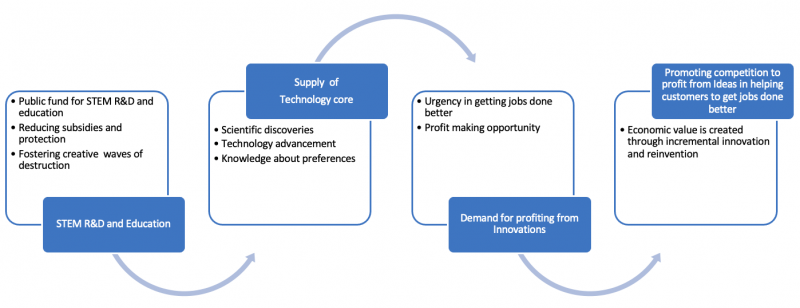
It has been found that STEM policy should be more than expanding education, offering R&D funding, and performing economic analysis for adopting technology solutions. It should include a technology policy for succeeding in the innovation race. Besides, STEM policy should find a linkage with the agenda of addressing competitiveness issues in formulating industrial policy. Furthermore, technology transfer should be integral to technology and industrial policies for adding value through STEM. Due to a lack of natural correlation, innovation ecosystem development is not good enough. With the given reality, the focus of Engineering Economics and Management should be on winning the global invention, reinvention and innovation race for tuning the perceived importance of STEM into economic prosperity.
For Further Clarity
- Rise and Fall of Nations—Role of STEM
- Technology for sustainable development—turning the curse into a blessing
- Sustained Economic Growth—leveraging STEM
- STEM Policy—driving prosperity
- Technology Policy—from adoption to advancement
- Industrial Policy—competitiveness from STEM
- Technology Transfer—from importer to exporter
- Innovation Ecosystem—strategy and policy




