Skill development focuses on developing a learned ability to perform certain things well. Understanding the necessity of skill development is not difficult. But for upskilling and reskilling, should rely on keep going to skill development institutions? Transformation of work due to technology has been making the future of work uncertain—resulting in reskilling and upskilling needs. Certain statistics suggest that 50% of all employees will need reskilling by 2025. But with the growing role of automation, is there much scope for upskilling? However, there is an increasing need for soft skills in addition to hard skills. For example, a recent study finds that ninety-two percent of professionals responded that soft skills matter as much or more than hard skills. Furthermore, soft skills are increasingly crucial to organizational success. Due to weakness in soft skills, the productivity of hard skills suffers.
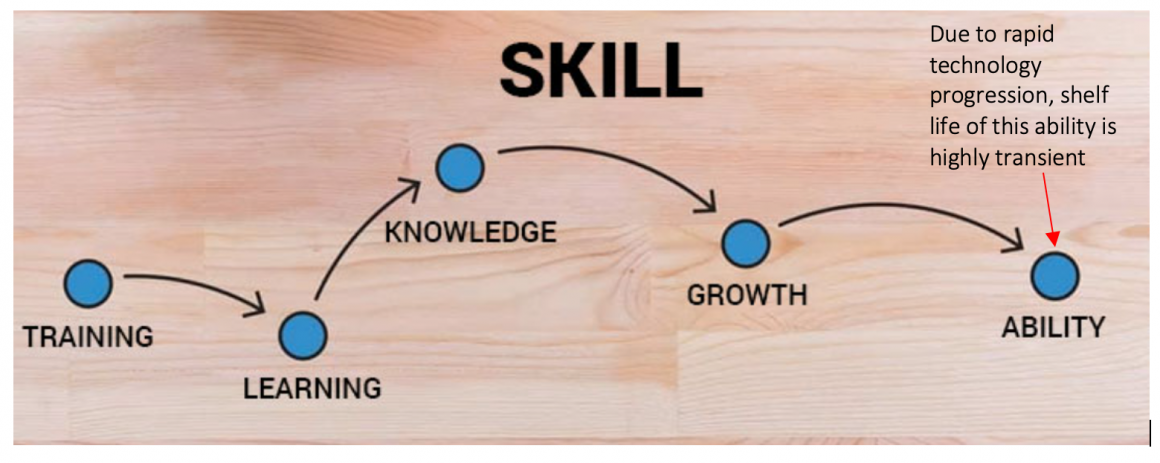
The core of skill development is to develop expertise in creating productive tasks and performing them, primarily by leveraging science and technology. Hence, skill development is an ongoing process. It’s a process of identifying skill gaps in the target population and ensuring the development of the skills. Organizations that encourage skill development have a stronger workforce. It influences employees’ motivation and improves productivity. But due to rapid technological progression, skills that are in high demand today end up suffering from quick erosion. Hence, conventional means of skill development through going to schools, again and again, does not appear to be appropriate. Besides, sharpening of soft skills increases the effectiveness and efficiency of the applications occupation-specific technical skills.
Skill Types: Hard skills vs. Soft skills
Two broad categories of skills are (i) Soft and (ii) hard skills. Some of the common soft skills are active listening, problem-solving, interpersonal skills, time management, communication, leadership, etc. Other soft skills are creativity, Passion for Perfection, critical thinking, integrity, teamwork, empathy, and willingness to learn. Hard skills or technical skills are abilities specific to the job or industry. We acquire these skills through education, training, and on-job experiences. For example, how to write computer code or solving a mathematical problem is a hard skill. On the other hand, soft skills belong to social or people skills; it’s embedded in personality traits.
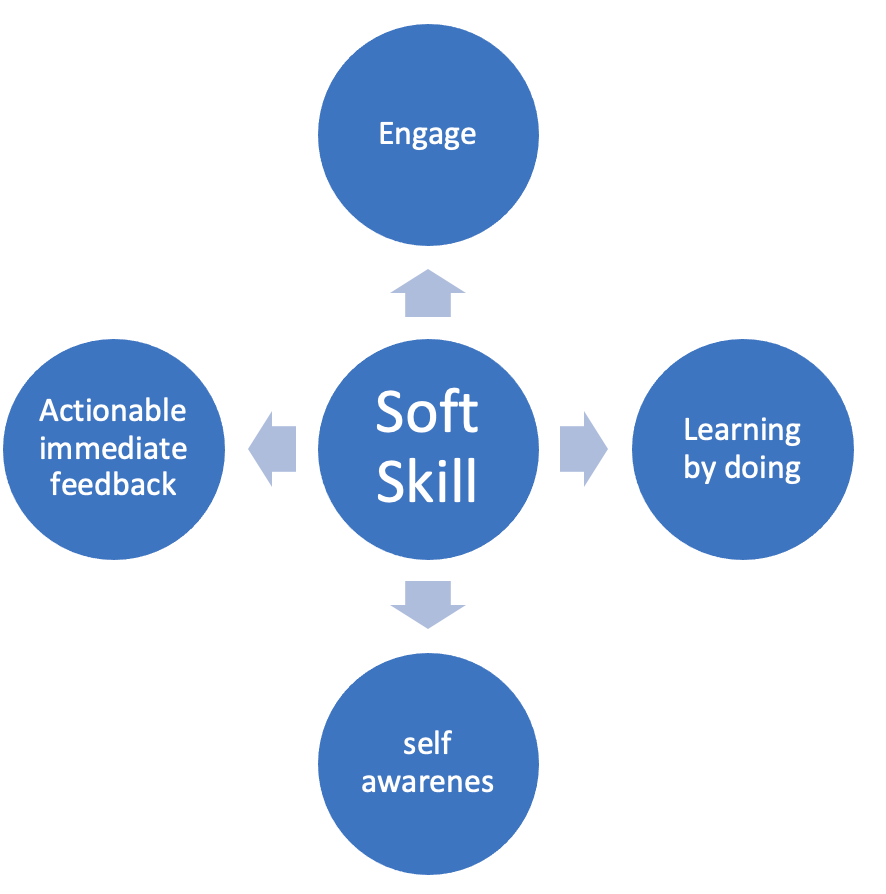
Although soft skills are highly valuable, they are quite hard to develop. Furthermore, in most cases, soft skills augment hard skills. For example, attention to detail skills enables the reduction of errors in applying hard skills. Similarly, passion for perfection is a vital skill in fine-tuning the application of any hard skills. Hence, skill development should have a balanced focus on both types of skills. Due to the weakness of soft skills, the investment made in developing hard skills runs the risk of wasteful investment. For example, in the absence of empathy, innovations for leveraging science and engineering skills may become not-so-desirable products by the customers. Some of the approaches of sharpening soft skills are (i) engaging, (ii) learning by doing, (iii) self-awareness, and (iv) providing actionable feedback. By adopting an appropriate process of hard kill development, we can sharpen soft skills too.
Interdisciplinary skills (IS) are becoming increasingly important. Studies find that interdisciplinary thinking and acting is one of the most critical skill requirements. Increasing technological complexity and adoption of innovative digital technologies in a wide range of sectors and fields, including agriculture, medicine, health, education, and banking, has been increasing the importance of IS.
Skill development predictions:
Technology development leads to the transformation of work. Hence, changing skill development has become natural, resulting in skill gaps. To address it, we need skill development initiatives and programs. According to the world economic forum, the top ten skills of 2025 are (i) analytical thinking and Innovation, (ii) active learning and learning strategies, (iii) complex problem solving, (iv) critical thinking and analysis, (v) creativity, originality, and initiative, (vi) leadership and social influence, (vii) technology use, monitoring and control, (viii) technology design and programming, (ix) Resilience, stress tolerance, and flexibility, and (x) reasoning, problem-solving and ideation.
According to the WEF report, 50 percent of all employees will need reskilling due to technology adoption. Does it mean that employers need to roll out massive reskilling training? Interestingly, the vast majority of business leaders, as high as 94%, expect that employees will pick up new skills on the job. Hence, on-job learning, self-learning, and life-long learning are getting important attributes of a career.
innate abilities and genesis of skill development:
Soft skills are not only useful as a category of skills; they largely influence the effectiveness and efficiency of the application of hard skills. For example, communication and teamwork skills influence how well someone applies his or her software programming skills. Similarly, passion for perfection seriously affects the quality of ideas someone generates to find innovative use of technology.
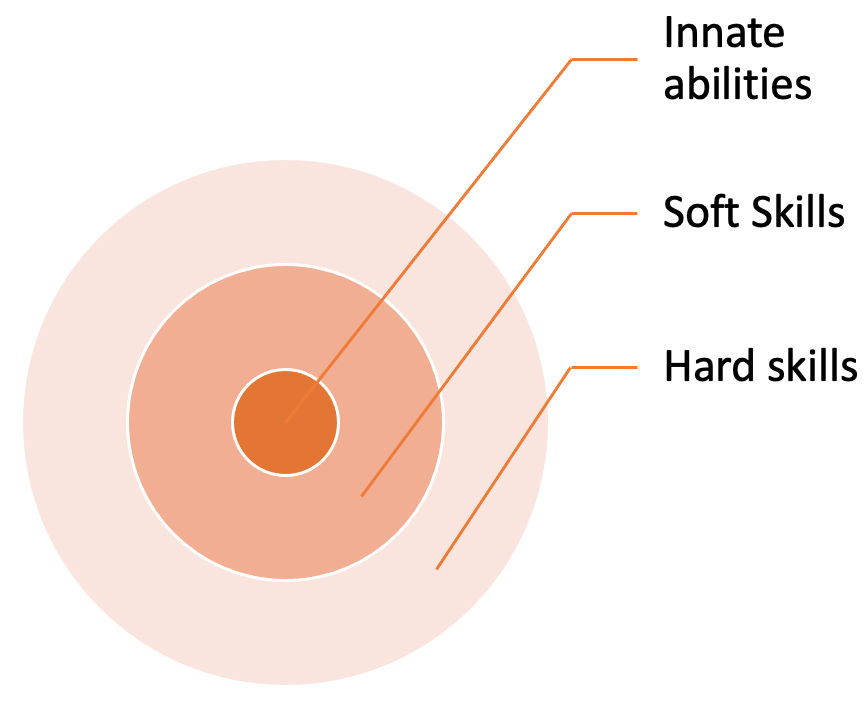
Interestingly, more or less, all soft skills have roots in human beings’ innate abilities. They are our by-born abilities. According to the O*Net database, we have 52 of them. Sharpening these innate abilities is vital to improving the application of technical, functional, or hard skills. Furthermore, many factory jobs mostly demand innate ability-centric soft skills. Hence, without participation in education, training, and skill development programs, the unskilled labor force of Bangladesh, Indonesia, and many other less developed countries have been producing textile products and shoes for the export market. Sharpening of these soft skills will contribute to productivity improvement and slow down the invasion of robotics and automation.
Besides, great inventors like Steve Jobs and Thomas Alva Edison relied on their innate abilities to show magical innovation performance. They did not learn that magical power through education or training. Human beings started gathering knowledge, generating ideas, inventing technologies, and innovating products and processes through innate abilities. Subsequently, the necessity of replicating innovations by operating the production process started demanding skills from replicators and operators.
Inventions and innovations create skill demand and transformation:
Human beings have an inherent urge and ability to gather knowledge and invent technologies. Innovators use those technologies to innovate products and processes for offering better alternatives to customers in Getting jobs done. Of course, gathering knowledge, inventions, and innovations demand skills. Besides, producing copies of innovations by operating production processes requires a new skill set.
Furthermore, human beings are on a relentless journey in finding better means. Hence, they are finding a better alternative to the products and processes they have been using now. For these reasons, products like Television or processes like checking in the airports have been evolving. This evolution has been redefining human roles in producing, operating, and consuming innovations. Hence, skill transformation is an endless phenomenon.
Switching work area demands reskilling:
People do not stick to the same job upon entering the job market. Even they change the occupation. For example, someone entering the job market as a computer programmer may switch for being an investment banker. For making such a switch, there is a need for reskilling.
Skill development focuses on reducing the skill gap in performing target tasks. For sure, technology advancement is at the core of changing skill demand. The adoption of technologies in innovating new products and processes and updating existing ones have created the demand for new skills and transformed existing ones. Besides, people have a tendency to switch jobs, professions, and careers. Hence, skill development has been an ongoing effort.
Furthermore, in addition to hard skills, we should pay attention to honing soft skills. As formal training does not work much, the process of developing hard skills should include learning by doing, engaging, giving feedback, and including fieldwork for sharpening soft skills. Although, there has been growing emphasis on separate skill development institutions, initiatives, and training programs, perhaps, the focus should be on integrating education with real-life problem solving, on-job training, and self-learning. Besides, broad undersigning or knowledge about the underlying science of products and process forms the underpinning of self-learning. Hence, occupation-specific skill development should not overlook the importance of broad-based knowledge.
...welcome to join us. We are on a mission to develop an enlightened community by sharing the insights of Wealth creation out of technology possibilities as reoccuring patters. If you like the article, you may encourage us by sharing it through social media to enlighten others.



